Gastroshiza: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Insights
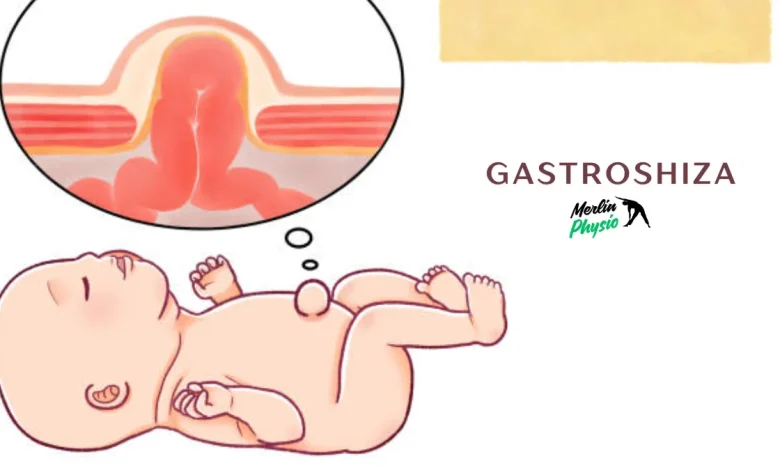
Introduction to Gastroshiza
Gastroshiza is a rare but serious congenital condition that affects newborns, leaving parents with many questions and concerns. Imagine the shock of learning that your baby has a defect where their intestines develop outside of their body. This alarming situation can be daunting, but understanding gastroshiza helps to navigate this challenging landscape. With early detection and modern medical advancements, families facing this diagnosis have more hope than ever before.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what gastroshiza really is, its causes and symptoms, how it’s diagnosed and treated today, as well as the long-term management strategies for affected children. Knowledge is power when it comes to health challenges like these—let’s dive into the world of gastroshiza together!
What Causes Gastroshiza?
Gastroshiza is a complex condition, and its exact cause remains somewhat elusive. It typically occurs during early fetal development when the abdominal wall fails to close properly.
Several factors may contribute to this defect. Genetic predispositions can play a significant role, as certain hereditary conditions might increase the risk of gastroshiza in families.
Environmental influences are also considered important. Maternal health factors such as nutritional deficiencies or exposure to specific medications during pregnancy may heighten the chances of developing this condition.
Advanced maternal age has been linked with increased risks for various congenital anomalies, including gastroshiza. Furthermore, lifestyle choices like smoking or substance abuse can negatively impact fetal development.
Understanding these potential causes helps healthcare providers offer better guidance and support for expectant mothers at risk.
Common Symptoms of Gastroshiza
Gastroshiza presents a range of symptoms that can vary in intensity. The most noticeable sign is the protrusion of abdominal organs through an opening beside the umbilical cord. This condition typically becomes apparent at birth.
Parents may also observe additional signs such as difficulty feeding or respiratory distress in their newborns. These issues arise when vital organs are exposed and not functioning normally.
In some cases, gastroshiza can lead to complications like infection or impaired blood flow to the affected organs.
Early detection is critical for managing these symptoms effectively and reducing potential risks. Keeping a vigilant eye on your child’s health during those first days after birth can be pivotal in ensuring timely medical intervention.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing gastroshiza typically begins with a thorough prenatal ultrasound. This imaging technique can reveal the presence of abdominal organs located outside the body. If detected, further evaluations may be necessary to assess potential complications.
Once diagnosed, treatment options vary based on several factors, including the size of the defect and the baby’s overall health. Surgical intervention is essential for most cases of gastroshiza. The procedure usually occurs shortly after birth to reposition the affected organs back into the abdomen.
In some instances, doctors might opt for a staged approach. This involves gradually placing organs back inside over time if they cannot fit immediately due to swelling or other issues.
Post-surgery care is crucial and often includes monitoring for infections and ensuring proper nutrition as healing progresses. Each case requires a tailored plan that prioritizes both immediate needs and long-term outcomes.
Modern Advancements in Gastroshiza Treatment
Recent years have seen significant advancements in the treatment of gastroshiza. Innovative surgical techniques are now employed to repair the abdominal wall defect more effectively. Surgeons utilize minimally invasive methods, which result in less trauma and quicker recovery times.
Additionally, the use of tissue engineering is gaining traction. Researchers are exploring ways to create synthetic or biological materials that can promote better healing and integration with surrounding tissues.
Post-operative care has also evolved. Enhanced monitoring technologies allow for real-time assessments of a patient’s recovery process, helping healthcare providers intervene promptly if complications arise.
Moreover, multidisciplinary teams play a crucial role in managing gastroshiza cases. Specialists from various fields collaborate to provide comprehensive care tailored to each patient’s needs.
These advancements reflect a commitment to improving outcomes for those affected by this condition. They pave the way for more effective treatments and ultimately better quality of life for patients dealing with gastroshiza.
Recovery and Long-Term Management of Gastroshiza
Recovery from gastroshiza often begins immediately after surgical intervention. The initial days can be challenging, as infants may require intensive care to stabilize their condition.
Post-surgery, parents should be aware of the need for close monitoring. Regular follow-ups with pediatric specialists are crucial to track growth and development. Nutrition plays a pivotal role in recovery. Specialized feeding methods might be necessary to ensure that the baby gets adequate nourishment.
Long-term management focuses on addressing potential complications that may arise, such as digestive issues or infections. Support groups and resources can provide valuable assistance for families navigating these challenges.
Encouraging developmental milestones is essential during recovery. Engaging with healthcare providers about any concerns will help foster an environment where children thrive despite their early health struggles. Each child’s journey is unique, making personalized care plans vital for successful long-term outcomes.
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment for Gastroshiza
Early detection and treatment of gastroshiza play a crucial role in improving outcomes. This congenital condition, characterized by an abdominal wall defect, can lead to significant complications if not addressed promptly.
Identifying symptoms early allows for timely intervention, which is essential for the health of affected infants. Medical professionals recommend regular prenatal screenings to spot potential issues before birth. For those diagnosed after birth, immediate care can mitigate risks and enhance recovery prospects.
Parents and caregivers should remain vigilant and informed about gastroshiza. Understanding the signs and seeking medical attention as soon as possible can make a difference in managing this condition effectively.
With advancements in medical technology and surgical techniques, the outlook for individuals with gastroshiza has improved significantly over recent years. Emphasizing awareness among expecting parents can also contribute to better overall outcomes.
Fostering open communication between healthcare providers and families is vital in navigating through diagnosis and treatment options efficiently. By prioritizing education on gastroshiza, we empower families with knowledge that could potentially save lives.




