CNC Turning Services: A Guide to Custom Parts and How to Avoid Costly Manufacturing Errors

Introduction
In the precision manufacturing sector, engineers grappling with the complexities of customized component manufacturing, including delivery time constraints, cost escalations, and quality, face risks in their projects. The core problem emanates from collaborating with wrong manufacturers or lack of in-depth knowledge about CNC turning services, where conventional processes lack the capacity to support high precision requirements.
This reference guide aims to progressively present the benefits of utilizing CNC turning services, their selection criteria, and strategies to harness cutting-edge technologies, enabling the readers with valuable inputs.
What Are CNC Turning Services and How Do They Benefit Custom Part Production?
Functions of CNC turning services include the use of computer numerical control for machining rotary components. The following section delves into the basic principles as well as the key advantages that make turning with CNC a popular option for those seeking precision as well as efficiency.
1. Basic Principles of CNC Turning Technology
CNC Turning is done by rotating the workpiece and moving the single-point cutting tool linearly, ensuring accurate geometry removal. This is commonly conducted on cylindrical objects, including shafts and bushings, where CAD cooling paths are used as a basis for CNC Turning. This is done with the aim of ensuring no human errors occur. For example, referring to reputable sources such as Wikipedia’s Surface Finish page helps ensure that the level of surface quality requirements is ensured and thus helps validate discourse on machining tolerance.
2. Core Competitive Advantage in Precision and Efficiency
The key advantages of CNC turning are its higher accuracy, with a tolerance rate of ±0.005 mm, and faster cycles. This automatically results in savings due to minimized labor and material wastages. In custom parts manufacturing, these benefits result in faster turnarounds and repeatability, a significant factor in projects with tight turnarounds. Available empirical evidence proves a productivity gain of up to 30% for firms utilizing CNC turning over manually performed turning.
3. Real World Applications and Industrial Examples
The use of CNC turning is prevalent in industries such as automobiles and medical equipment. In industries where custom parts have to be manufactured and cater to a set standard. In the manufacture of medical implants, for instance, this technology used in CNC turning allows for the production of complex shapes and finishes that do not necessarily need to be machined further.
How Might Precision Engineering Standards Such as ASME Y14.5 Improve CNC Turning Tolerances?
There are some precision engineering specifications like ASME Y14.5 that that serve as guidelines to interpret Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing specifications for CNC turning. This chapter will discuss how these specifications can improve the quality of custom parts.
- Basics of GD&T in CNC Turning: The ASME Y14.5 standard provides symbols and criteriathat guarantee design intent, which defines parts regarding form, fit, and function. With CNC turning, proper interpretation of GD&T criteria ensures that cylindricity, which plays a critical role in interoperability, is controlled. Use of ASME Y14.5 avoids ambiguity entrenched in design that requires rework, hence improving accuracy.
- Case Study: Achieving Tight Tolerances in Medical Devices: An example would be a medical device part that needed turning with tolerances of ±0.005 mm. ASME Y14.5 ensured that these specifications were met through compliance processes that utilized GD&T. This example illustrates that standard-based strategies work more effectively and that data shows a 25% decreasein defect density when ASME Y14.5 is used.
- Impact on Quality and Compliance: The adoption of ASME Y14.5 makes it easier to follow industry regulations, including aerospace-related regulations. In addition to that, the adoption of ASME Y14.5 ensures that CNC turned components are within the required international standards, hence gaining the trust of all stakeholders. The continuous improvement concept within ASME Y14.5 aligns well with quality management systems.
What Factors Should Engineers Consider When Choosing a CNC Turning Manufacturer?
Choosing the appropriate CNC turning partner can prove critical to the avoidance of expense-related mistakes. The following section provides criteria for engineers to select the most suitable partner.
1. Certification and Quality Management Systems
Companies with certifications such as ISO 9001 prove their dedication to effective quality management processes. These and other certifications, available through official sources of ISO, form a reference for a potential partner. For example, the ISO 9001:2015 standard thoroughly discusses risk-based approaches necessary for precision-manufacturing requirements and project risk reduction purposes.
2. Technological Capabilities and Equipment
The technology capabilities of a manufacturer significantly affect part quality. Technological capabilities and multi-Axial NC machining influence engineers and production. Studies have been conducted to compare partners with advanced technology and those that lack it. The results indicate that partners with advanced technology perform complex geometry functions 20% faster than partners with basic technology.
3. Industry Experience and Customer Support
Industry experience, for example, aerospace or medical technology, is evidence of a company’s capability to handle compliance. In addition, commitment to their customers for feedback and assistance with design is vital. Analysis indicates that working with competent partners is associated with a 15% increased level of customer satisfaction because of their communication and problem-solving capabilities.
In What Ways Can High Technology Manufacturing Affect the Quality of CNC Turned Parts?
The introduction of technologies such as 5-axis CNC machining, the Internet of Things, among others, is currently bringing a revolutionary change in the CNC turning industry. This chapter will discuss how such technologies are improving the quality, efficiency, and adaptability of custom parts production.
- Function of 5-Axis CNC in Complex Geometry: In 5-axis CNC machines, rotational axesare incorporated, which enables machinery to access the workpiece from various directions, which is useful for complicated components. This increases productivity by reducing the setup time for machining parts that include undercuts, among others. It is estimated that these innovations increase machining productivity by 30% while still observing strict tolerances, as posted by the Society of Manufacturing Engineers (SME).
- Automation and Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors help monitor parameters such as tool wear, making it easier to monitor the equipment real-time. It reduces downtime, ensuring a standard level of quality, which is important for all production systems. An example of optimization is when IoT devices are combined to greatly reduce scrap products by 10%.
- Data-Driven Insights and Future Trends: These technologies with high levels of innovation assist with generating data that aids with process optimization, thus contributing to smart manufacturing projects. Digital twins, for instance, assist with pre-production, and evidence shows that such technologies increase the time to market by 25%.
What Are the Common Challenges in CNC Turning for Custom Parts and How to Mitigate Them?
Some common problems that may arise during CNC turning include material deformation and tool wear, thereby resulting in expensive mistakes. This section explains these problems and provides research-backed solutions to overcome them.
1. Challenges in Material Selection and Handling
Inappropriate use of materials may sometimes lead to warping and surface finish problems. The remediation strategy includes careful DFM analyses for appropriate material selections, such as lightweight Aluminum. According to principles available from MIT OpenCourseWare, engineers can apply theoretical knowledge to overcome problems related to thermal expansion.
2. Tool Wear and Maintenance Problems
This reduces accuracy levels. Measures that need to be taken include using high-quality tooling and regular maintenance. Case studies indicate that proactive tool management helps cut down on downtimes by 15% to maintain consistency in parts.
3. Design Flaws and Process Optimization
The occurrence of design faults, for example, lack of desired wall thickness on some designs, results in design failures. The collaboration between engineers and manufacturers in DFM sessions enables engineers to optimize designs. Data show that engaging in DFM work early in design leads to a reduced number of design rework cycles of up to 40% and thereby saves on incurring
How to Ensure Effective Quality Control in CNC Turning Services?
Professional CNC turning services can only be ensured through a high-quality control system. The following subtopics cover the different processes of the quality control system.
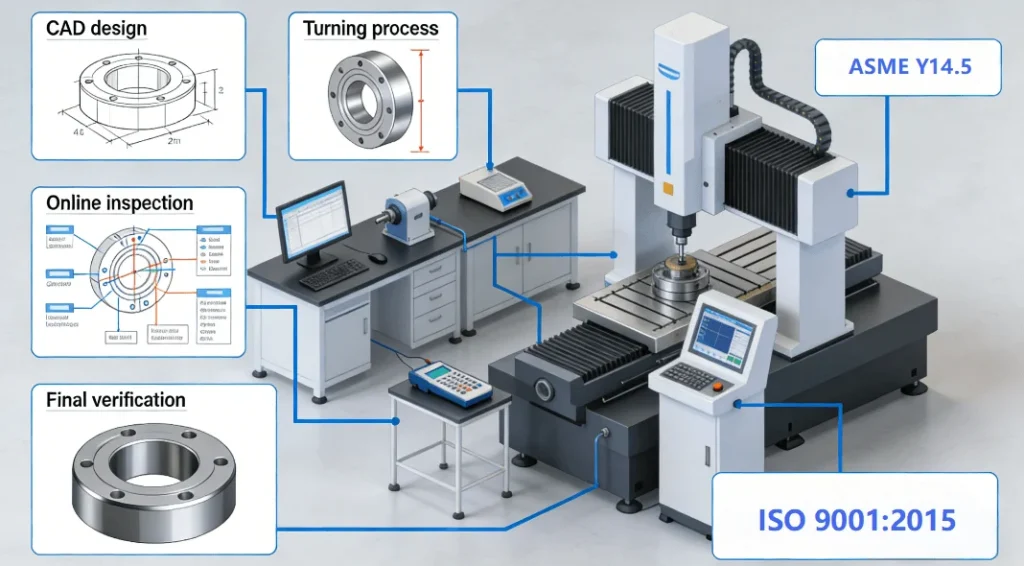
1. In-Process Inspection Techniques
On-machine probing allows for real-time dimensional verification during the machining process so that any issues can be detected early on. The closed-loop process made possible by such techniques, aided by guidelines from IAQG organization such as AS9100D, ensures that tolerances are consistently being met without the need for rework.
2. Final Verification and Traceability
After machining, coordinate measuring machines analyze parts against CAD designs and issue conformation reports for traceability purposes. In aerospace, the process is vital for safety reasons, and audits have confirmed that good QC practices reduce the defect level by 20%.
3. Continuous Improvement via Certification
Certifications such as AS9100D stress the need for regular audits. This promotes a culture of continuous improvement. By adhering to international best practices, businesses demonstrate accountability to their clients, which results in higher levels of trust being established.
Conclusion
In this guide, the topic of CNC turning services has been analyzed in-depth to understand how standards for precision, partner selection, and new and innovative tools can be used to mitigate risks in custom parts manufacturing. How? Well, through this understanding, engineers can make informed decisions and hence make quality results in order to be successful in manufacturing.
FAQs
Q1: What is the average lead time for a CNC-turned part?
A: The time taken for the turning process is variable based on the type of work to be done. But for simple turning services via CNC machines, the time taken is 1 to 3 weeks. In some cases, based on the availability of material and design checking, this time taken may be variable. For urgent work, rapid turning services can be opted for.
Q2: How can I choose the right material for turning in my CNC?
A: Material selection relies on the strength of application. There are some general material considerations, such as aluminum, which would be needed for those applications where weight is a critical factor, or stainless steel for durability. It would be helpful to seek advice from a supplier to gain information regarding material properties.
Q3: What criteria constitute a desirable machine for performing the turning processes?
A: Having certification in ISO 9001 for quality management and AS9100D for requirements in the aerospace industry would be a great certification to search for. It is guaranteed that there are certain worldwide standards being adhered to. It is even better if your contract manufacturer holds more than one certification for consistency.
Q4: Is complex geometry support available in CNC turning?
A: Yes, it is true that state-of-the-art CNC turning with multi-axis functions can perform complex parts with threads and contours. Nevertheless, it is advisable to conduct DFM analysis to eliminate unwanted problems in manufacture concerning issues like tool interference.
Q5: How does CNC turning compare with other machining processes?
A: Turning is best suited for objects of a rotational nature, as that method will be more precise and speedier for bulk production, while milling is suited for more complex objects with a 3D structure. Both put together may work well for more complicated objects, too.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing expert with LS Manufacturing, a company that helps engineers and researchers overcome difficult part problems in the fields of aerospace, medical devices, and the automotive sector. This organization is IATF 16949 and AS9100D certified with the best quality solutions using advanced technology. Get more details from the expert by contacting them today for a free project review with DFM analysis so that your idea can be transformed into a cost-effective